| نویسندگان | Farshad Boorboor Ajdari*, Abolfazl Fathollahi Zonouz*, Ali Heydari, Hassan Shokoui Mehrabani, Mehdi Shakourian-Fard, Ganesh Kamath, Fatemeh Ghasemi, and Meisam Kahrizi |
|---|---|
| نشریه | J. Phys. Chem. C |
| نوع مقاله | Original Research |
| تاریخ انتشار | 2023-04-24 |
| رتبه نشریه | ISI |
| نوع نشریه | الکترونیکی |
| کشور محل چاپ | ایران |
چکیده مقاله
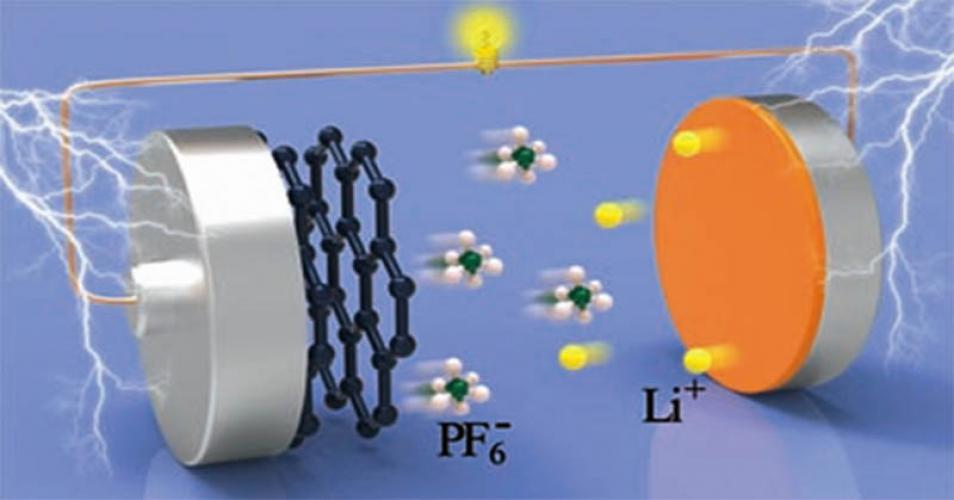
Concerns over recyclability, performance, and safety have grown as the use of commercial Li-ion batteries to meet our energy needs has increased. Electrolytes may aid in increased flammability, capacity loss, and safety. Dimethyl methyl phosphonate (DMMP), a flame retardant, and dopamine hydrochloride (DOP) are utilized to increase the cycle life and graphite anode compatibility. The optimal additive formulation (5% wt DMMP and 0.1% wt DOP) reduces inflammability and increases cycle life and reversible capacity (99.14%). Molecular dynamics simulations provide a comprehensive atomistic account of the dynamics of Li+ ion solvation in the electrolytes and in the presence of additives. Dopamine and DMMP increase the Li-ion solvation-free energy in the electrolyte formulation. While increasing the Li-ion conductivity, additive addition reduces the electrolyte viscosity and enables the formation of a smaller, stronger Li-DMMP-DOP complex than the larger Li-carbonate complex found in Li-neat electrolyte systems. When DMMP and DOP are added to the electrolyte, the carbonates are displaced from the Li-carbonate complex by these additives. The Li-ion solvating nature or compatibility was improved upon the addition of DMMP/DOP further aided by a faster diffusive behavior of the Li complex, which in part would be instrumental in enhancing the performance and safety of the battery electrolyte additive formulations. The modified electrolyte (DMMP 5% wt, DOP 0.1% wt) has a conductivity of 18.60 mS cm–1 and a low viscosity at 25 °C. This formulation was evaluated using graphite/NMC-532 cylindrical cells with commercial electrodes. The performance of the graphite/NMC-532 cells containing the modified electrolyte was comparable to those of regular electrolytes based on carbonates: ethylene carbonate/dimethyl carbonate/ethylmethylcarbonate (EC/DMC/EMC) (1:1:1) additions. These findings indicate that DOP and DMMP have a lower oxidation potential (4.3 V) than most commercial electrolytes (4.5 V), preventing cathode deterioration. These insights should pave the path for rational design of practical and cost-effective Li-ion battery electrolyte additive combinations aimed toward lower flammability and improved performance.
متن کامل مقاله
لینک دانلود فایل