| نویسندگان | Farshad Boorboor Ajdari* , Ali Hassan -nejad, Fereshteh Abbasi, Mohadeseh Jafari , Parnaz Asghari |
|---|---|
| نشریه | Automotive Science and Engineering (ASE) |
| شماره صفحات | 4496 |
| شماره مجلد | 14 |
| ضریب تاثیر (IF) | ثبت نشده |
| نوع مقاله | Full Paper |
| تاریخ انتشار | 2024-09-04 |
| رتبه نشریه | علمی - پژوهشی |
| نوع نشریه | الکترونیکی |
| کشور محل چاپ | ایران |
| نمایه نشریه | ISC |
چکیده مقاله
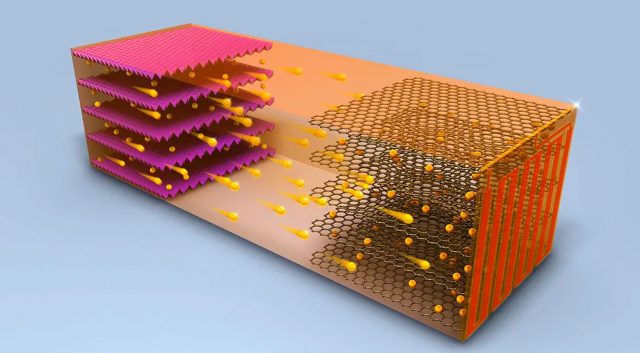
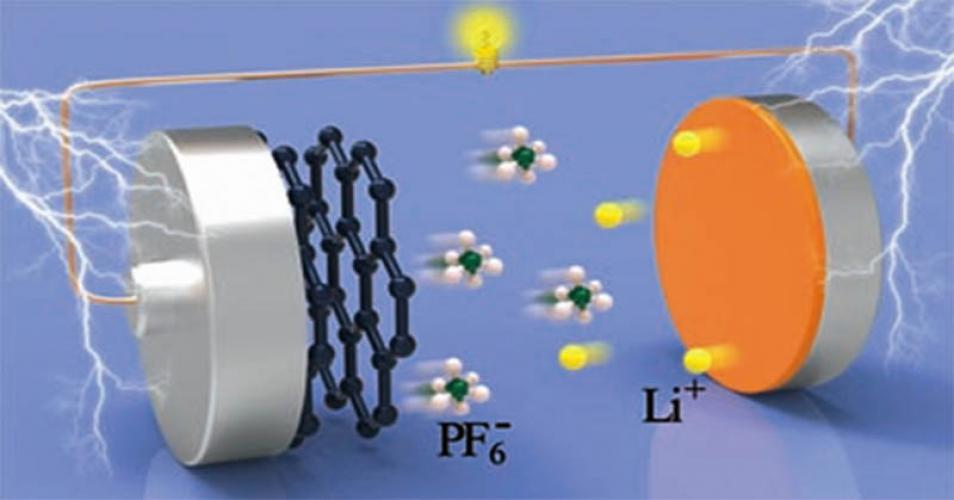
Today, the utilization of lithium -ion batteries (LIBs) has significantly increased as an energy storage technology. In recent years, the high demand for lithium for LIB has resulted in a significant increase in the consumption of lithium -containing materials. It is anticipated that the reduction of lithium due to the limited reserves of lithium will be one of the considerable challenges in the future. The lithium -ion battery industry's primary component is lithium, extracted from natural minerals and saline water. However, the extraction of lithium from natural minerals and saline water is a complex process requiring significant energy. Conversely, the number of batteries approaching the end of their lifespan is unavoidably increasing alarmingly. To address the obstacles that the lithium battery supply chain encounters, it is imperative that a variety of recycling technologies and methodologies be further developed. This article concentrates on technologies that can recycle lithium compounds from LIB through distinct processes and procedures. These stages are further divided into two pre - treatment phases and a lithium extraction stage. The lithium extraction stage is divided into three primary methods: pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy, and Direct. This review article quantitatively compares and analyzes each recycling method's processes, advantages, disadvantages, efficiency, price, environmental contamination, and degree of commercialization. This review can offer a suitable perspective to enhance this path.