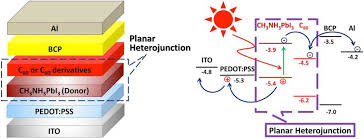
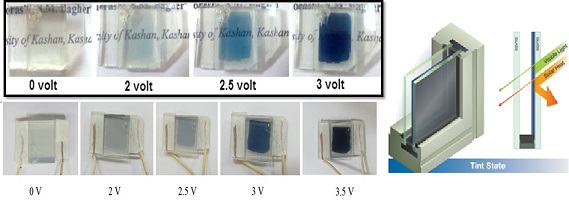
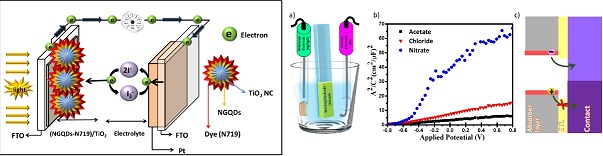
| نویسندگان | فاطمه عباسی,سیدمحمدباقر قریشی,پروین اسکندریان,حسین زابلیان |
|---|
| نشریه | J MATER SCI |
|---|
| ضریب تاثیر (IF) | ثبت نشده |
|---|
| نوع مقاله | Full Paper |
|---|
| تاریخ انتشار | 2022-04-11 |
|---|
| رتبه نشریه | علمی - پژوهشی |
|---|
| نوع نشریه | الکترونیکی |
|---|
| کشور محل چاپ | ایران |
|---|
| نمایه نشریه | JCR |
|---|
چکیده مقاله
Herein, an inexpensive and efficient device structure using copper phthalocyanine (CuPc) as a dopant into tris-(8-hydroxyquinoline) aluminum (Alq3) is introduced for near-infrared (NIR) organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). An optimized green OLED was first fabricated, and then the device's electroluminescent performance was compared with its simulation results gained via the APSYS (Advanced Physical Model of Semiconductor Devices) method. After confirming the simulation results, the emission spectra and external quantum efficiency (EQE) were investigated for OLEDs doped with different concentrations of CuPc using the APSYS program. Electroluminescence was observed near 1.1 µm, following the transitions from CuPc's low-lying triplet state (T1) to its ground state (S0). A further optimized NIR OLED with 2wt% CuPc demonstrated superior performance to other structures via the efficient energy transfer from the host excited states to the NIR phosphors, realizing a maximum EQE value of 0.11%, and radiance of 316 μW/cm2.