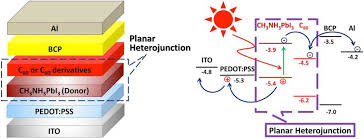
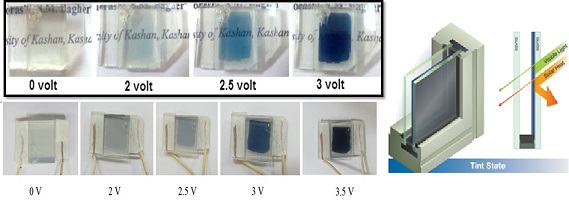
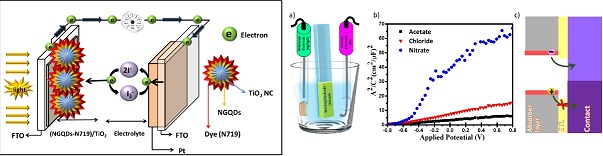
| نویسندگان | مریم هدایتی,سعید علیایی,سیدمحمدباقر قریشی |
|---|
| نشریه | J ELECTRON MATER |
|---|
| شماره صفحات | 1454 |
|---|
| شماره مجلد | 49 |
|---|
| ضریب تاثیر (IF) | ثبت نشده |
|---|
| نوع مقاله | Full Paper |
|---|
| تاریخ انتشار | 2019-11-26 |
|---|
| رتبه نشریه | علمی - پژوهشی |
|---|
| نوع نشریه | الکترونیکی |
|---|
| کشور محل چاپ | ایران |
|---|
چکیده مقاله
The split of the sunlight spectrum by the bandgap energy of multi-junction
solar cells is a highly effective way to increase solar cell efficiency. The reason
is that the energy of photons is effectively absorbed, and there is a reduction in
solar cell loss. In this contribution, we report on the performance of a doublejunction
copper gallium diselenide/copper indium gallium diselenide (CGS/
CIGS) solar cell with a cadmium sulfide (CdS) buffer layer simulator. The J–V
characteristics and the external quantum efficiency were simulated under
AM1.5 illumination. Increased efficiency was seen as a result of the change in
the thickness of layers and different molar ratio amounts of gallium, and the
optimal amount of each factor was obtained. In this study, a single CGS solar
cell was used as the top cell and a single CIGS solar cell as the bottom cell in
the tandem configuration, which showed conversion efficiencies of 16.175%
and 15.696%, respectively. Finally, solar cell efficiency of 32.3% was obtained
in the double-junction state, an increase of 6% compared with the reference
cell.